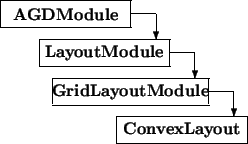




Baseclasses

Definition
The class ConvexLayout represents the layout algorithm Convex by Goos Kant [Kan96].
This algorithm draws a planar, triconnected graph G straight-line without crossings. G must not contain self-loops or multiple edges. All faces are drawn convex, the grid layout size is at most (2n - 4) x (n - 2) for a graph with n nodes (n > = 3).
The algorithm runs in two phases. In the first phase, a so-called shelling order (also called canonical ordering) for triconnected planar graphs is computed. Then, the vertices are placed incrementally according to the shelling order.
General Information
| Algorithm | |
| name | Convex |
| long name | Convex (Kant) |
| author | G. Kant |
| Implementation | |
| author | C. Gutwenger |
| date | March 1997 |
| version | 2.0 |
Pre- and Postcondition
| precondition | = | { planar, triconnected, simple, noselfloops } |
| postcondition(PRE) | = | { straight - line, nocrossings, convex } |
Optional Parameters Instances of ConvexLayout provide the following optional parameters:
#include < AGD/ConvexLayout.h >
Creation
| ConvexLayout | L | creates an instance L of type ConvexLayout. |
Operations
Standard Interface (Inherited Methods) The detailed description of these methods can be found in the manual entries of the base classes (LayoutModule, GridLayoutModule).
| bool | L.check(const graph& G, AgdKey& p) | |
| void | L.call(const graph& G, LayoutInterface& A) | |
| void | L.call(const graph& G, face f, LayoutInterface& A) | |
| void | L.call_grid(const graph& G, GridLayout& gl) | |
| void | L.call_grid(const graph& G, face f, GridLayout& gl) | |
| IRect | L.bounding_box() | |
| void | L.set_mapper(const GridCoordinateMapper& gcm) |
Access to Options
| bool | L.size_opt() | |
| void | L.size_opt(bool so) | |
| double | L.base_ratio() | |
| void | L.base_ratio(double br) |
Implementation
The computation of the layout takes time
![]() (n),
where n is the number of nodes of the input graph.
(n),
where n is the number of nodes of the input graph.




© Copyright 1998-2001, Algorithmic Solutions Software GmbH. All rights reserved.
2001-08-13