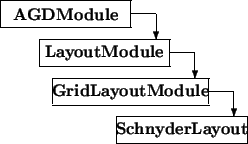




Baseclasses

Definition
The class SchnyderLayout represents the layout algorithm by Schnyder [Sch90].
This algorithm draws a planar graph G straight-line without crossings. G must not contain self-loops or multiple edges. The grid layout size is (n - 2) x (n - 2) for a graph with n nodes (n > = 3).
The algorithm runs in three phases. In the first phase, the graph is augmented by adding new artificial edges to get a triangulated plane graph. Then, a partition of the set of interior edges in three trees (also called Schnyder trees) with special orientation properties is derived. In the third step, the actual coordinates are computed.
General Information
| Algorithm | |
| name | Schnyder |
| long name | Schnyder |
| author | W. Schnyder |
| Implementation | |
| author | D. Ambras, D. Alberts |
| date | February 1997 |
| version | |
Pre- and Postcondition
| precondition | = | { planar, simple, noselfloops } |
| postcondition(PRE) | = | { straight - line, nocrossings } |
#include < AGD/SchnyderLayout.h >
Creation
| SchnyderLayout | L | creates an instance L of type SchnyderLayout. |
Operations
Standard Interface (Inherited Methods) The detailed description of these methods can be found in the manual entries of the base classes (LayoutModule, GridLayoutModule).
| bool | L.check(const graph& G, AgdKey& p) | |
| void | L.call(const graph& G, LayoutInterface& A) | |
| void | L.call(const graph& G, face f, LayoutInterface& A) | |
| void | L.call_grid(const graph& G, GridLayout& gl) | |
| void | L.call_grid(const graph& G, face f, GridLayout& gl) | |
| IRect | L.bounding_box() | |
| void | L.set_mapper(const GridCoordinateMapper& gcm) |
Implementation
The computation of the layout takes time
![]() (n),
where n is the number of nodes of the input graph.
(n),
where n is the number of nodes of the input graph.




© Copyright 1998-2001, Algorithmic Solutions Software GmbH. All rights reserved.
2001-08-13