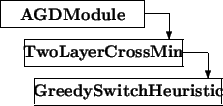




Baseclasses

Definition
The greedy switch heuristic passes over all consecutive pairs of vertices and switches them if this decreases the number of crossings (see Eades and Kelly [EK86]).
General Information
| Algorithm | |
| name | Greedy-Switch |
| long name | Greedy-Switch (Eades,Kelly) |
| author | P. Eades, D. Kelly |
| Implementation | |
| author | M. Krüger, Th. Ziegler |
| date | March 1998 |
| version | 1.0 |
Pre- and Postcondition
| precondition | = | |
| postcondition(PRE) | = |
#include < AGD/GreedySwitchHeuristic.h >
Creation
| GreedySwitchHeuristic | M | creates an instance M of type GreedySwitchHeuristic. |
Operations
Standard Interface (Inherited Methods) The detailed description of these methods can be found in the manual entries of the base class (TwoLayerCrossMin).
| bool | M.check(const leda_graph& G, const Layer& L, AgdKey& p) | |
| void | M.init(const leda_graph& G, const Hierarchy& H) | |
| void | M.call(const leda_graph& G, Layer& L) | |
| void | M.cleanup() |
Implementation
Let nL denote the number of nodes on the changeable layer
and mL the number of edges between the fixed and the changeable layer.
The algorithm computes in a preprocessing step a so-called
crossing matrix, which takes time
![]() (nLmL).
For the running time of the actual crossing reduction algorithm,
we quote the paper: ``The time complexity of this algorithm is
hard to compute, because it depends on the number of switchings
required to reach a stable ordering. However, since the total
number of crossings is at most m2, we can at least
guarantee that the algorithm is
(nLmL).
For the running time of the actual crossing reduction algorithm,
we quote the paper: ``The time complexity of this algorithm is
hard to compute, because it depends on the number of switchings
required to reach a stable ordering. However, since the total
number of crossings is at most m2, we can at least
guarantee that the algorithm is
![]() (nLmL2).''
(nLmL2).''




© Copyright 1998-2001, Algorithmic Solutions Software GmbH. All rights reserved.
2001-08-13