| leda_face |
H.get_external_face() |
returns the external face.
|
| int |
H.get_angle(leda_edge e) |
returns the angle edge e forms with its successor.
|
| leda_string |
H.get_string(leda_edge e) |
returns the bit string for edge e.
|
| direction |
H.dir(leda_edge e) |
returns the direction of edge e.
|
| bool |
H.hor(leda_edge e) |
returns true if edge e is horizontal (direction north).
|
| bool |
H.ver(leda_edge e) |
returns true if edge e is vertical (direction west).
|
| int |
H.number_of_bends() |
returns the number of bends
|
| bool |
H.simple() |
returns true if H is simple, i.e., the number of bends is zero, and false otherwise.
|
| bool |
H.is_cage(leda_face f) |
returns true, if f is an artificial face, i.e., a face corresponding to a vertex in the original graph.
|
| int |
H.output_level() |
returns the output level
|
| void |
H.set_external_face(leda_face f) |
| |
|
sets the external face to f.
|
| void |
H.set_angle(leda_edge e, int a) |
| |
|
sets the angle between e and the following edge to a.
|
| void |
H.set_string(leda_edge e, leda_string s) |
| |
|
sets the bit string for edge e to s.
|
| void |
H.set_string(leda_edge e, char c, int n) |
| |
|
sets the bit string for edge e to cn.
|
| void |
H.add_convex_bend(leda_edge e) |
| |
|
adds a 90o bend to edge e.
|
| void |
H.add_concave_bend(leda_edge e) |
| |
|
adds a 270o bend to edge e.
|
| leda_face |
H.expand(leda_node v) |
replaces vertex v by face c. Returns c.
|
| leda_node |
H.collapse(leda_face f) |
is the undo of expand. Face f will be replaced by its former vertex v.
|
| leda_edge |
H.split(leda_edge e) |
splits egde e and updates the data structure accordingly.
|
| void |
H.normalize() |
transforms the representation into a simple representation
by replacing each bend by a vertex and updating the data structure.
|
| void |
H.dissect() |
dissects all inner faces in subfaces of rectangular shape.
|
| void |
H.undissect() |
is the inverse operation of dissect. Deletes all previously inserted virtual vertices and edges.
|
| void |
H.orientate() |
assigns consistent directions to the edge segments.
|
| void |
H.orientate(leda_edge e, direction d) |
| |
|
assigns consistent directions to the edge segments. The reference
edge e gets direction d.
|
| void |
H.output_level(int o) |
sets the output level to o.
Reasonable values are
o 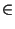 [0...10].
o = 0 causes the algorithm to run in silent mode,
a value o > = 10 will create the greatest
possible amount of output. [0...10].
o = 0 causes the algorithm to run in silent mode,
a value o > = 10 will create the greatest
possible amount of output.
|
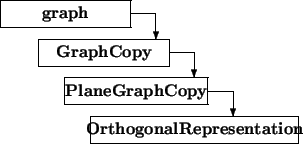





![]() E(G) the following information can be accessed:
E(G) the following information can be accessed: