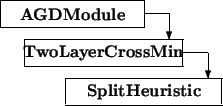




Baseclasses

Definition
The module SplitHeuristic chooses a pivot vertex v and places every other vertex to the left or right of v according to whether it would make fewer crossings. This step is applied recursively to order the left hand side and right hand side of v (see Eades and Kelly [EK86]).
General Information
| Algorithm | |
| name | Split |
| long name | Split (Eades,Kelly) |
| author | P. Eades, D. Kelly |
| Implementation | |
| author | M. Krüger, Th. Ziegler |
| date | March 1998 |
| version | 1.0 |
Pre- and Postcondition
| precondition | = | |
| postcondition(PRE) | = |
#include < AGD/SplitHeuristic.h >
Creation
| SplitHeuristic | M | creates an instance M of type SplitHeuristic. |
Operations
Standard Interface (Inherited Methods) The detailed description of these methods can be found in the manual entries of the base class (TwoLayerCrossMin).
| bool | M.check(const leda_graph& G, const Layer& L, AgdKey& p) | |
| void | M.init(const leda_graph& G, const Hierarchy& H) | |
| void | M.call(const leda_graph& G, Layer& L) | |
| void | M.cleanup() |
Implementation
Let nL denote the number of nodes on the changeable layer
and mL the number of edges between the fixed and the changeable layer.
The algorithm computes in a preprocessing step a so-called
crossing matrix, which takes time
![]() (nLmL).
The actual crossing reduction algorithm takes time
(nLmL).
The actual crossing reduction algorithm takes time
![]() (nLlognL). Both steps are implemented in the
call()-method.
(nLlognL). Both steps are implemented in the
call()-method.




© Copyright 1998-2001, Algorithmic Solutions Software GmbH. All rights reserved.
2001-08-13