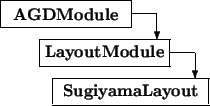




Baseclasses

Definition
The class SugiyamaLayout represents a general framework for drawing graphs with the hierarchical drawing method suggested by Sugiyama, Tagawa, and Toda [STT81]. This method works in three phases:
General Information
| Algorithm | |
| name | Sugiyama |
| long name | Sugiyama |
| author | K. Sugiyama, S. Tagawa, M. Toda |
| Implementation | |
| author | C. Gutwenger, M. Krüger |
| date | March 1998 |
| version | 2.0 |
Pre- and Postcondition
| precondition | = | { noselfloops, directed } |
| postcondition(PRE) | = |
Exchangeable Modules Instances of type SugiyamaLayout provide the following module options:
| guaranteed precondition: | {noselfloops, directed} |
| required postcondition: | |
| initial module: | LongestPathRanking |
| guaranteed precondition: |
{noselfloops, directed}, |
| required postcondition: | |
| initial module: | BarycenterHeuristic |
| guaranteed precondition: | |
| required postcondition: | |
| initial module: | FastHierarchyLayout |
Optional Parameters Instances of SugiyamaLayout provide the following optional parameters:
#include < AGD/SugiyamaLayout.h >
Creation
| SugiyamaLayout | L | creates an instance L of type SugiyamaLayout. |
Operations
| void | L.ext_call(const leda_graph& G, leda_node_array<int>& rank, LayoutInterface& A) | |
| calls L for graph G with layout interface A. Uses the level assignment defined by rank. | ||
| void | L.reduce_crossings(GraphCopy& GC, Hierarchy& H) | |
| calls only the crossing reduction step for graph copy GC and hierarchy H. | ||
| int | L.number_of_crossings() | returns the number of crossings in the layout produced by a preceding call. |
Standard Interface (Inherited Methods) The detailed description of these methods can be found in the manual entries of the base class (LayoutModule).
| bool | L.check(const graph& G, AgdKey& p) | |
| void | L.call(const graph& G, LayoutInterface& A) |
Access to Options
| bool | L.set_ranking(const RankAssignment& M) | |
| bool | L.set_cross_min(const TwoLayerCrossMin& M) | |
| bool | L.set_comp_coord(const HierarchyLayoutModule& M) | |
| bool | L.init_order() | |
| void | L.init_order(bool b) | |
| int | L.runs() | |
| void | L.runs(int n) | |
| int | L.fails() | |
| void | L.fails(int n) | |
| bool | L.transpose() | |
| void | L.transpose(bool b) |
Example
Example 1: We use only the crossing reduction phase of the Sugiyama algorithm with the Split heuristic and our own level assignment.
#include <LEDA/graphwin.h>
#include <AGD/SugiyamaLayout.h>
#include <AGD/SplitHeuristic.h>
#include <AGD/DfsRanking.h>
#include <AGD/Hierarchy.h>
#include <AGD/GraphCopy.h>
void reduce_crossings(graph& G)
{
node_array<int> rank(G);
// assign a non-negative level to each node in G
// we simply use a rank assignment module
DfsRanking().call(G,rank);
// build the hierarchy
GraphCopy GC(G);
Hierarchy H(GC,rank);
// call crossing minimization
SugiyamaLayout sugiyama;
sugiyama.set_cross_min(SplitHeuristic());
sugiyama.reduce_crossings(GC,H);
// the positions of the nodes (in GC) on each layer
// can now be accessed via H
}
Example 2: We compute a layout in a GraphWin with
our own level assignment.
#include <LEDA/graphwin.h>
#include <AGD/SugiyamaLayout.h>
#include <AGD/DfsRanking.h>
void call_with_ranking(GraphWin& GW)
{
graph& G = GW.get_graph();
node_array<int> rank(G);
// assign a non-negative level to each node in G
// we simply use a rank assignment module
DfsRanking().call(G,rank);
// compute layout in GW
GraphWinInterface A(GW);
SugiyamaLayout sugiyama;
sugiyama.ext_call(G,rank,A);
}




© Copyright 1998-2001, Algorithmic Solutions Software GmbH. All rights reserved.
2001-08-13